Azure 容器实例(ACI)提供了在 Azure 中运行容器的最简捷方式,它不需要用户配置任何虚拟机或其它高级服务。ACI 适用于快速突发式增长和资源调整的业务,但功能相对比较简单。对于需要完整容器集群编排功能的场景建议使用 ACS 或 AKS。
ACI 的优势包括
- 不需要用户配置和管理虚拟机就可以提供虚拟机级别的安全隔离
- 启动快速
- 支持自定义大小
- 支持绑定公网IP和持久化存储
- 支持Linux 和 Windows 容器
- 支持容器组将多个容器运行在一起(类似于 Kubernetes Pod),它们共享相同的生命周期、网络协议栈、IP地址以及存储
- 可以通过aci-connector-k8s将 ACI 作为 Kubernetes 集群的一个无限 Node 使用
注意:目前 ACI 仅在 westus、eastus 和 westeurope 等区域开放。
入门示例
# 创建资源组
az group create --name myResourceGroup --location eastus
# 创建容器(对应 docker run)
az container create --name mycontainer --image microsoft/aci-helloworld --resource-group myResourceGroup --ip-address public
# 查询容器(对应 docker ps或 docker inspect)
az container show --name mycontainer --resource-group myResourceGroup [-o table/json]
# 查询容器日志
az container logs --name mycontainer --resource-group myResourceGroup
# 删除容器
az container delete --name mycontainer --resource-group myResourceGroup
容器组
支持容器组将多个容器运行在一起(类似于 Kubernetes Pod),它们共享相同的生命周期、网络协议栈、IP地址以及持久化存储。容器组常以 sidecar 模式运行一组功能管理的容器,如应用程序和监控容器、应用程序和日志容器等。
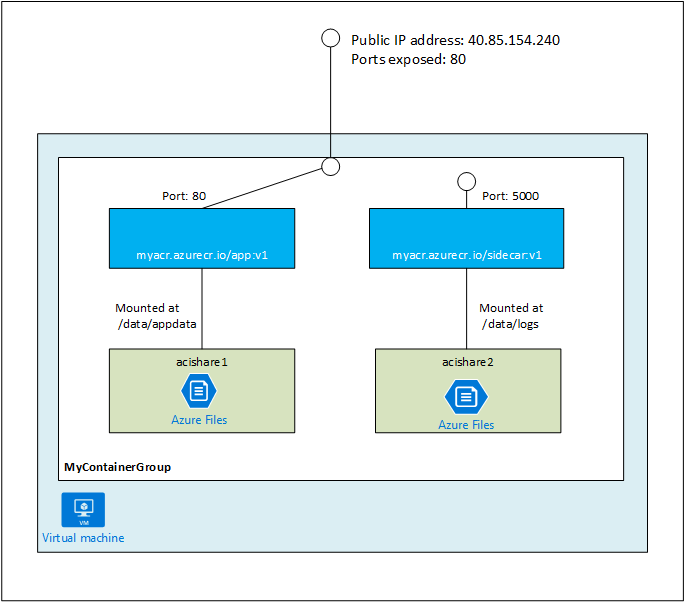
目前,容器组仅支持以模板的方式来运行。模板格式为
{
"$schema": "https://schema.management.azure.com/schemas/2015-01-01/deploymentTemplate.json#",
"contentVersion": "1.0.0.0",
"parameters": {
},
"variables": {
"container1name": "aci-tutorial-app",
"container1image": "microsoft/aci-helloworld:latest",
"container2name": "aci-tutorial-sidecar",
"container2image": "microsoft/aci-tutorial-sidecar"
},
"resources": [
{
"name": "myContainerGroup",
"type": "Microsoft.ContainerInstance/containerGroups",
"apiVersion": "2017-08-01-preview",
"location": "[resourceGroup().location]",
"properties": {
"containers": [
{
"name": "[variables('container1name')]",
"properties": {
"image": "[variables('container1image')]",
"resources": {
"requests": {
"cpu": 1,
"memoryInGb": 1.5
}
},
"ports": [
{
"port": 80
}
]
}
},
{
"name": "[variables('container2name')]",
"properties": {
"image": "[variables('container2image')]",
"resources": {
"requests": {
"cpu": 1,
"memoryInGb": 1.5
}
}
}
}
],
"osType": "Linux",
"ipAddress": {
"type": "Public",
"ports": [
{
"protocol": "tcp",
"port": "80"
}
]
}
}
}
],
"outputs": {
"containerIPv4Address": {
"type": "string",
"value": "[reference(resourceId('Microsoft.ContainerInstance/containerGroups/', 'myContainerGroup')).ipAddress.ip]"
}
}
}
而部署容器组也需要使用 az group deployment 命令
az group deployment create --name myContainerGroup --resource-group myResourceGroup --template-file azuredeploy.json
部署成功后就可以通过 az container 命令来查看或操作容器了(使用 --container-name 指定操作的是哪个容器)。
私有镜像
私有镜像可以存储在 Azure 容器注册表(ACR)中。
# Create ACR
az acr create --resource-group myResourceGroup --name <acrName> --sku Basic --admin-enabled true
# Login
az acr login --name <acrName>
# Tag the image.
az acr list --resource-group myResourceGroup --query "[].{acrLoginServer:loginServer}" --output table
docker tag azure-vote-front <acrLoginServer>/azure-vote-front:redis-v1
# push image
docker push <acrLoginServer>/azure-vote-front:redis-v1
# List images.
az acr repository list --name <acrName> --output table
使用私有镜像创建容器时,需要通过 --registry-password 选项给每个容器设置密码(比 docker login 麻烦一些):
# Query password.
az acr credential show --name <acrName> --query "passwords[0].value"
# Create container.
az container create --name aci-tutorial-app --image <acrLoginServer>/aci-tutorial-app:v1 --cpu 1 --memory 1 --registry-password <acrPassword> --ip-address public --ports 80 -g myResourceGroup
或者在部署模板(比如上述容器组示例)中设置
"imageRegistryCredentials": [
{
"server": "[parameters('imageRegistryLoginServer')]",
"username": "[parameters('imageRegistryUsername')]",
"password": "[parameters('imageRegistryPassword')]"
}
]
持久化存储
必须先创建 Azure 文件共享,才能将其用于 Azure 容器实例。
# Create the storage account
az storage account create -n mycontainerstorage -g myResourceGroup --sku Standard_LRS
# Export the connection string as an environment variable, this is used when creating the Azure file share
AZURE_STORAGE_CONNECTION_STRING=$(az storage account show-connection-string -n mycontainerstorage -g myResourceGroup -o tsv)
# Create the share
az storage share create -n myacishare
# Get storage account key.
STORAGE_ACCOUNT="mycontainerstorage"
STORAGE_KEY=$(az storage account keys list --resource-group myResourceGroup --account-name mycontainerstorage --query "[0].value" -o tsv)
持久化存储也是需要通过模板来引用,创建下面的模板文件
{
"$schema": "https://schema.management.azure.com/schemas/2015-01-01/deploymentTemplate.json#",
"contentVersion": "1.0.0.0",
"parameters": {
"storageaccountname": {
"type": "string"
},
"storageaccountkey": {
"type": "securestring"
}
},
"resources":[{
"name": "hellofiles",
"type": "Microsoft.ContainerInstance/containerGroups",
"apiVersion": "2017-08-01-preview",
"location": "[resourceGroup().location]",
"properties": {
"containers": [{
"name": "hellofiles",
"properties": {
"image": "seanmckenna/aci-hellofiles",
"resources": {
"requests": {
"cpu": 1,
"memoryInGb": 1.5
}
},
"ports": [{
"port": 80
}],
"volumeMounts": [{
"name": "myvolume",
"mountPath": "/aci/logs/"
}]
}
}],
"osType": "Linux",
"ipAddress": {
"type": "Public",
"ports": [{
"protocol": "tcp",
"port": "80"
}]
},
"volumes": [{
"name": "myvolume",
"azureFile": {
"shareName": "myacishare",
"storageAccountName": "[parameters('storageaccountname')]",
"storageAccountKey": "[parameters('storageaccountkey')]"
}
}]
}
}]
}
最后部署容器
# deploy container group
az group deployment create --name hellofilesdeployment --template-file hellofiles.json --resource-group myResourceGroup --parameters storageaccountname=$STORAGE_ACCOUN storageaccountkey=$STORAGE_KEY
# list container
az container list -g myResourceGroup -o table
Kubernetes集成
aci-connector-k8s 可以将 ACI 作为 Kubernetes 集群的一个无限 Node 使用。
下载 aci-connector-k8s 源码后,可以运行 examples/generateManifest.py 命令自动生成一个部署 aci-connector 的配置(不包含RBAC配置)。
python3 generateManifest.py -g myResourceGroup -s <my-subscription-id> -l westus
而在开启RBAC的系统中,需要配置相应的权限,比如使用下面的部署文件
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: aci-connector
namespace: default
spec:
replicas: 1
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: aci-connector
spec:
serviceAccount: aci-connector
containers:
- name: aci-connector
image: microsoft/aci-connector-k8s:latest
imagePullPolicy: Always
env:
- name: AZURE_CLIENT_ID
value: <your-client-id>
- name: AZURE_CLIENT_KEY
value: <your-client-key>
- name: AZURE_TENANT_ID
value: <your-tenant-id>
- name: AZURE_SUBSCRIPTION_ID
value: <your-subsription-id>
- name: ACI_RESOURCE_GROUP
value: <your-resource-group>
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: aci-connector
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: List
items:
- apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
name: "aci-connector"
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["namespaces"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["pods", "pods/status"]
verbs: ["get","list","watch","create","patch","update","delete"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["nodes", "nodes/status"]
verbs: ["get","list","watch","create","patch","update","delete"]
- apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
name: "aci-connector"
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: "aci-connector"
subjects:
- apiGroup: ""
kind: ServiceAccount
name: "aci-connector"
namespace: "default"
这样,Deployment部署后,很快就可以发现它自动创建了一个 aci-connector 的 Node
# kubectl get node aci-connector
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
aci-connector Ready <none> 1m v1.6.6
这样,Pod可以通过指定 nodeName 或者容忍 taint azure.com/aci=NoSchedule 调度到ACI上面:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: nginx
labels:
run: nginx
spec:
containers:
- image: nginx
imagePullPolicy: Always
name: nginx
dnsPolicy: ClusterFirst
nodeName: aci-connector
# kubectl get pods -l run=nginx -o wide
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE
nginx 1/1 Running 0 28s x.x.x.x aci-connector
# az container list -g myResourceGroup -o table
Name ResourceGroup ProvisioningState Image IP:ports CPU/Memory OsType Location
------ --------------- ------------------- ------- ---------------- --------------- -------- ----------
nginx myResourceGroup Succeeded nginx x.x.x.x:80 1.0 core/1.5 gb Linux westus