Shanghai,
CN-31
【摘要】1. 前言Together we will ensure that Kubernetes is a strong and open container management framework for any application and in any environment, whether i… 阅读全文
【摘要】ansible简介ansible是与puppet、saltstack类似的集群管理工具,其优点是仅需要ssh和Python即可使用,而不像puppet、saltstack那样都需要客户端。与puppet类似,ansible也支持丰富的功能:批量执行支持模块化,支持playbook(相比puppet还… 阅读全文
Kubernetes v1.2以前,如果想要对某个NODE(也就是Kubelet和Docker所在的机器)进行维护(比如升级Docker或者内核等)又不想影响运行中的Pod的话,需要手动做很多的步骤:
... ➦Kubernetes network policy
Kubernetes社区(确切的说是Kubernetes Network SIG [1])正在讨论Network Policy Proposal,以实现SDN、网络隔离、IP Overlapping等[2]复杂的网络需求。
... ➦The main idea of the paper is that the typical failover architecture used when moving from a single datacenter to multiple datacenters doesn’t work well in practice. What does work, where work means using fewer resources while providing high availability and consistency, is a natively multihomed architecture:
... ➦Our current approach is to build natively multihomed systems. Such systems run hot in multiple datacenters all the time, and adaptively move load between datacenters, with the ability to handle outages of any scale completely transparently. Additionally, planned datacenter outages and maintenance events are completely transparent, causing minimal disruption to the operational systems. In the past, such events required labor-intensive efforts to move operational systems from one datacenter to another
Docker annonced Docker Datacenter (DDC) at Februrary 23. It is an integrated, end-to-end platform for agile application development and management from the datacenter to the cloud.
With Docker Datacenter, organizations are empowered to deploy a Containers as a Services (CaaS) on-premises or in your virtual private cloud. A CaaS provides an IT managed and secured application environment of content and infrastructure where developers can build and deploy applications in a self service manner.
... ➦Alpine Linux
随着Alpine Linux被越来越多的官方镜像使用,我们有必要了解一下Alpine Linux到底是个什么鬼。
Alpine Linux 是一个面向安全应用的轻量级 Linux 发行版。它采用了musl libc和busybox以减小系统的体积和运行时资源消耗,同时还提供了自己的包管理工具apk。Alpine Linux的内核都打了grsecurity/PaX补丁,并且所有的程序都编译为Position Independent Executables (PIE) 以增强系统的安全性。
... ➦终于等到了Docker for Mac。如之前期待的,体验真的很棒:
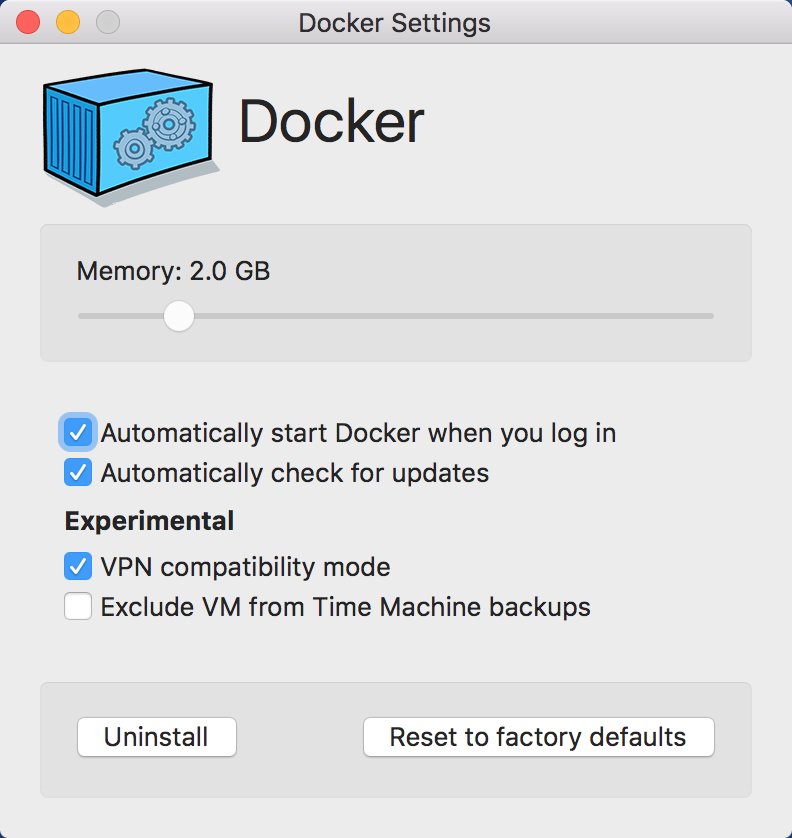
/var/run/docker.sock,这样客户端默认情况下就会走它的API;但也可以通过环境变量告诉docker CLI调用其他Docker Daemon的API(比如docker-machine管理的vm等)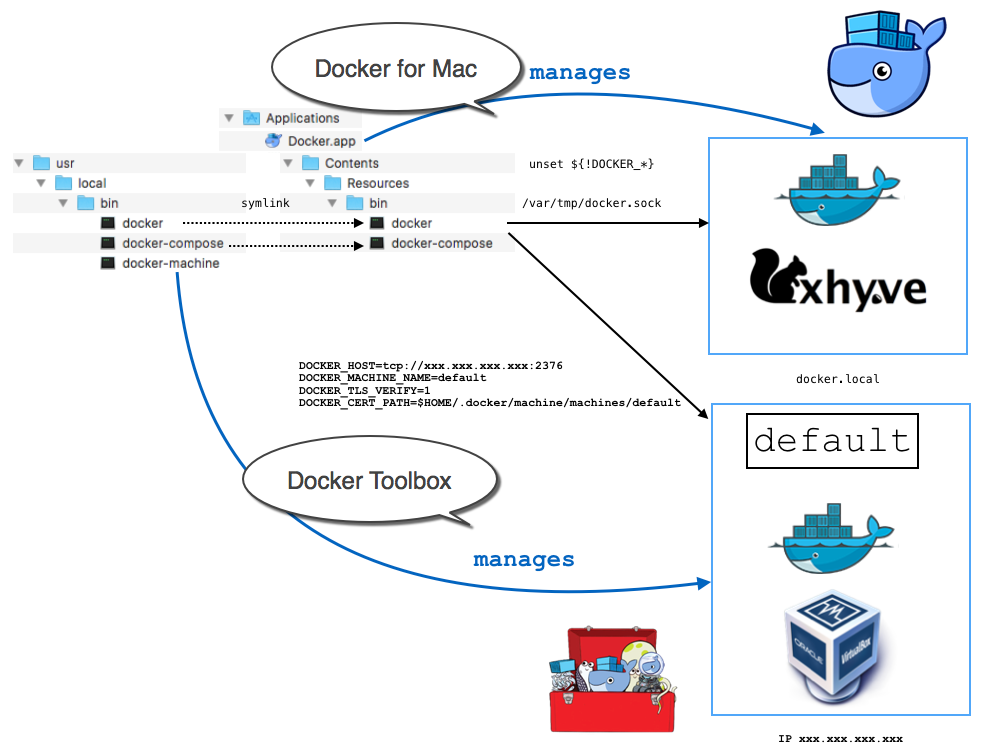
Google的Fergus Henderson在Software Engineering at Google中介绍了Google的软件工程实践。
源码仓库
Blaze分布式构建系统
... ➦2月28日,AWS工程师在排查Northern Virginia (US-EAST-1) Region的一个S3计费问题时,因敲错了一条playbook的参数而误删了大量的s3控制服务引发了4小时的故障。这个误操作影响了两个S3的核心系统:
... ➦